The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity in Financial Technology
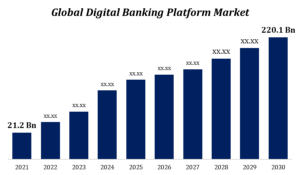
n today’s increasingly digital world, financial technology, or fintech, is revolutionizing how we manage, invest, and move money. From mobile banking and digital wallets to peer-to-peer lending and blockchain, fintech innovations are making financial services more accessible, efficient, and user-friendly. However, as fintech continues to evolve and integrate into every aspect of our financial lives, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated.
Cybersecurity is now a critical concern for fintech companies, financial institutions, and consumers alike. With the rise of sophisticated cyberattacks and the ever-growing volume of sensitive financial data being processed online, protecting digital assets and maintaining trust in these technologies has become paramount. This blog explores the growing importance of cybersecurity in fintech, the challenges the industry faces, and the strategies being employed to safeguard the future of digital finance.
1. Why Cybersecurity Matters in Fintech
Fintech companies operate at the intersection of finance and technology, managing vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal information, banking details, and transaction histories. This makes them prime targets for cybercriminals. A successful cyberattack on a fintech company can lead to severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and, most critically, a loss of trust among customers.
As the fintech industry continues to grow, so does the threat landscape. Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated, using advanced tactics such as phishing, ransomware, and data breaches to exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems. The increasing use of cloud computing, mobile devices, and interconnected systems further expands the attack surface, making it more challenging to protect against cyber threats.
2. Key Cybersecurity Challenges in Fintech
a. Data Breaches
Data breaches remain one of the most significant cybersecurity challenges for fintech companies. Hackers target databases containing sensitive customer information, such as social security numbers, credit card details, and bank account information. A breach can result in identity theft, financial fraud, and legal liabilities for the affected company.
b. Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing attacks involve tricking individuals into divulging confidential information by posing as a legitimate entity. In the fintech space, these attacks often target customers or employees through deceptive emails, messages, or websites. Social engineering tactics, such as impersonation or manipulation, can also be used to gain unauthorized access to systems or data.
c. Ransomware
Ransomware attacks involve encrypting a victim’s data and demanding payment in exchange for the decryption key. Fintech companies, due to the critical nature of their operations, are particularly vulnerable to ransomware attacks. Paying the ransom, however, does not guarantee data recovery and can encourage further attacks.
d. Third-Party Risks
Many fintech companies rely on third-party vendors and service providers for various aspects of their operations, from cloud hosting to payment processing. However, these third-party relationships can introduce additional cybersecurity risks. A breach at a vendor’s end can compromise the security of the fintech company’s systems and data.
e. Regulatory Compliance
The fintech industry is subject to strict regulations aimed at protecting consumer data and ensuring the security of financial transactions. Companies must navigate a complex web of regulatory requirements, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal consequences.
3. Strategies for Enhancing Cybersecurity in Fintech
To protect against the growing threat of cyberattacks, fintech companies must implement robust cybersecurity strategies. Here are some key approaches to enhancing cybersecurity in the fintech sector:
a. Strong Encryption
Encryption is a fundamental tool for securing sensitive data. Fintech companies should use strong encryption protocols to protect data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be easily accessed or deciphered by unauthorized parties.
b. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before accessing an account or system. This can include something the user knows (e.g., a password), something the user has (e.g., a smartphone), or something the user is (e.g., biometric data). MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if login credentials are compromised.
c. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Fintech companies should invest in advanced monitoring and threat detection systems that provide real-time visibility into network activity. These systems can detect suspicious behavior, such as unusual login attempts or unauthorized access to data, and respond to potential threats before they escalate into full-blown attacks.
d. Employee Training and Awareness
Human error remains one of the leading causes of cybersecurity incidents. Regular training and awareness programs can help employees recognize and respond to potential threats, such as phishing attempts or social engineering attacks. A well-informed workforce is an essential line of defense against cyber threats.
e. Incident Response Planning
Having a comprehensive incident response plan in place is critical for minimizing the impact of a cybersecurity breach. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of an attack, including communication protocols, data recovery procedures, and legal considerations. Regular testing and updates to the plan ensure that the organization is prepared to respond effectively to any security incident.
f. Collaboration with Regulators
Given the stringent regulatory environment in which fintech operates, companies should work closely with regulators to ensure compliance with cybersecurity standards and guidelines. Regular audits, assessments, and updates to security practices can help fintech companies stay ahead of regulatory requirements and avoid potential penalties.
4. The Future of Cybersecurity in Fintech
As fintech continues to evolve, so will the cybersecurity challenges it faces. The integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and quantum computing presents both new opportunities and risks. AI, for instance, can be used to enhance threat detection and automate responses, but it can also be weaponized by cybercriminals to launch more sophisticated attacks.
Blockchain technology, known for its security features, offers potential solutions for improving the security and transparency of financial transactions. However, as blockchain adoption grows, so do the risks associated with smart contract vulnerabilities and the need for secure key management.
The growing importance of cybersecurity in fintech cannot be overstated. As the industry continues to innovate and expand, fintech companies must prioritize the protection of their systems, data, and customers. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures and staying ahead of emerging threats, the fintech sector can continue to thrive and build trust in the digital financial ecosystem.