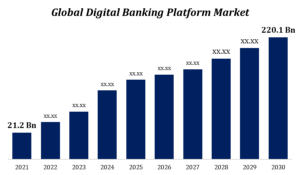
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Money, regularly known as DeFi, has arisen as possibly of the most thrilling and perilous movement in the monetary district. By utilizing blockchain improvement and sagacious plans, DeFi means to duplicate and update conventional cash related associations in a decentralized way, bypassing standard go betweens like banks and monetary establishments. By the by, what unequivocally is DeFi, and how should it change the universe of money? This blog looks at the essentials of DeFi, its key parts, advantages, downsides, and potential for reshaping the monetary scene.
What is Decentralized Money (DeFi)?
In light of the development of blockchain technology, Decentralized Cash (DeFi) suggests numerous financial applications that operate without delegates or central authority. Decentralized networks, primarily Ethereum, are used to provide financial services on DeFi platforms, in contrast to conventional financial frameworks that rely on banks, agents, and clearinghouses. Through keen agreements, which are self-executing contracts in which the arrangements of the seeing are directly translated into code, these organizations consolidate advancing, gaining, trading, and viable cash on the board.
The Main Pieces of DeFi Savvy Agreements: Shrewd agreements are the computerized scripts that sudden spike in demand for blockchain networks. They manage, examine, and maintain the nuances of financial transactions without human intervention. Adroit arrangements are utilized to supervise and complete credit, buy, and trade exchanges in DeFi.
Decentralized Trades (DEXs): In contrast to conventional trades, DEXs operate without a focal power. They simplify it for clients to exchange cryptographic types of cash with each other. Models coordinate Uniswap and SushiSwap. DEXs are more affordable and offer a more significant level of security than brought together trades.
Stages for Securing and Crediting: Clients can use DeFi platforms like Aave and Construct to either obtain assets through protection or credit their assets in order to earn interest. Calculations and shrewd agreements are utilized by these stages to set loan fees and oversee loaning pools.
Stablecoins: Computerized resources in stablecoins are fixed to a stable value, like the US dollar, to reduce unpredictability. DAI and USDC are two models. Since they give a steady method for exchanging and a store of critical worth inside the climate, stablecoins assume a urgent part in DeFi.
Stamping and developing yields: The practice of providing DeFi platforms with liquidity in exchange for additional tokens is known as yield farming. Checking entails participating in the community of a blockchain by acquiring assets to support projects with preferential endorsements, securing rewards, and so on.
Affirmation Procedures: Gambles related with hacking, savvy contract disappointment, and other unanticipated occasions are covered by Nexus Common and other DeFi protection stages. These stages work through decentralized mutuals and pools.
The advantages of DeFi accessibility: Anyone with a modernized wallet and a web affiliation can use DeFi stages. People from underserved or unbanked areas can now access financial institutions that were previously too far away thanks to this inclusion.
Transparency: All financial transactions and wise agreements are recorded on the blockchain on DeFi platforms, allowing clients to verify their legitimacy.
Diminished Expenses: DeFi arranges a large part of the time offer trades that are quicker and have lower charges since they incorporate no middle people. Clients can keep away from normal monetary charges like trade commissions and different accuses related of normal monetary administrations.
Interoperability: Different DeFi applications rely upon open-source shows, permitting them to relate dependably with other DeFi stages. This interoperability makes the monetary biological system more coordinated and strong.
Monetary Impact: Without relying on unified specialists, DeFi enables individuals to maintain control over their resources and financial decisions. Clients can unreservedly manage their portfolios, make trades, and partake in crediting or getting works out.
Uncertainty in the Regulator: Issues and Concerns The administrative climate for DeFi is right now advancing. Regulators and assemblies are trying to appreciate and address the consequences of decentralized financial systems. Vulnerability with respect to the administrative system might significantly affect the creation and execution of DeFi.
Security Dangers: Blockchain technology is safe, whereas DeFi platforms continue to be susceptible to danger. The DeFi industry has suffered significant losses as a result of hacking, coding errors, and smart contract vulnerabilities. Clients should practice wariness and direct top to bottom exploration preceding partaking in DeFi exercises.
Scalability: Due to the high volume of transactions, the Ethereum network, which is used by a number of DeFi stages, has experienced flexibility issues. A blocked network may result in longer trade times and higher costs. To determine these issues, propels like Ethereum 2.0 and layer-2 scaling are being made.
Complexity: The organic framework for DeFi is confusing and growing quickly. For beginners, the sheer number of stages, shows, and assets that clients ought to investigate can overwhelm. For making sound decisions in the DeFi sector, preparation and comprehension are essential.
Market Vulnerability: The worth of robotized resources in the DeFi environment can be especially impulsive. Value changes can affect the worth of security, loan costs, and generally speaking monetary dependability. Customers ought to be prepared for the volatile nature of the market.
The DeFi Upset’s Future Albeit still in its earliest stages, the DeFi upheaval can possibly adjust the monetary business. DeFi may be able to provide significantly more innovative approaches and entryways as development progresses and the natural framework develops. The future of DeFi will likely be heavily influenced by ongoing advancements in layer-2 scaling procedures, expanded security initiatives, and regulatory clarity.