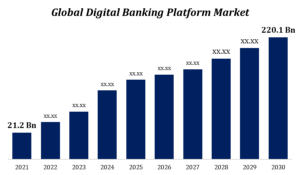
The Future of Financial Privacy
Financial privacy is a cornerstone of individual autonomy and trust in the financial system. As technology advances and financial transactions become increasingly digital, the concept of financial privacy is evolving, facing both new opportunities and challenges. This blog explores the future of financial privacy, examining emerging technologies, regulatory trends, and best practices for protecting personal financial information.
The Current State of Financial Privacy
Financial privacy concerns the protection of individuals’ financial information from unauthorized access and misuse. Traditionally, privacy was maintained through physical security measures and manual processes. However, with the rise of digital banking, online transactions, and data analytics, maintaining financial privacy has become more complex.
Key Aspects of Current Financial Privacy:
- Data Security: Safeguarding financial data from breaches and cyberattacks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to laws and regulations designed to protect consumer privacy.
- Consumer Control: Allowing individuals to control who has access to their financial information.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Financial Privacy
1. Advanced Encryption Techniques
Description: Encryption is the process of encoding data to prevent unauthorized access. Advanced encryption techniques are crucial for securing financial transactions and protecting sensitive information.
Technological Advances:
- Quantum-Resistant Encryption: Quantum computing poses a threat to traditional encryption methods. Developing encryption techniques that are resistant to quantum decryption is a priority for ensuring long-term data security.
- Homomorphic Encryption: This allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it, enhancing privacy while enabling data analysis.
Future Impact:
- Enhanced Security: Advanced encryption will bolster the security of financial transactions and protect against emerging threats.
- Privacy Preservation: Homomorphic encryption will enable secure data analysis without compromising individual privacy.
2. Blockchain Technology
Description: Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers. It offers transparency and security, which can enhance financial privacy in several ways.
Applications in Financial Privacy:
- Decentralized Identity Management: Blockchain can be used for secure and private management of digital identities, reducing reliance on centralized databases.
- Privacy Coins: Cryptocurrencies like Monero and Zcash use blockchain technology to provide enhanced privacy for transactions.
Future Impact:
- Improved Identity Protection: Blockchain-based identity systems will offer more control over personal data.
- Anonymous Transactions: Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies will enable confidential financial transactions.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Description: AI and machine learning can analyze vast amounts of data to detect patterns and anomalies. While this technology offers many benefits, it also presents challenges for financial privacy.
Applications in Financial Privacy:
- Fraud Detection: AI can identify fraudulent transactions by analyzing transaction patterns and behaviors.
- Data Anonymization: AI techniques can anonymize data to protect individual identities while allowing for data analysis.
Future Impact:
- Enhanced Fraud Prevention: AI-driven fraud detection will improve the security of financial systems.
- Balanced Privacy: Advanced anonymization techniques will protect privacy while enabling valuable data analysis.
4. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
Description: PETs are designed to protect data privacy by minimizing the amount of personal information collected and ensuring that data is handled securely.
Examples of PETs:
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: This cryptographic method allows one party to prove knowledge of a fact without revealing the fact itself.
- Secure Multi-Party Computation (SMPC): SMPC enables multiple parties to collaborate on data analysis without revealing their individual data.
Future Impact:
- Reduced Data Exposure: PETs will minimize the exposure of personal information during transactions and interactions.
- Enhanced User Control: Individuals will have more control over how their data is used and shared.
Regulatory Trends and Challenges
1. Evolving Data Protection Laws
Description: Data protection laws are continually evolving to address new privacy challenges. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) set standards for data protection and privacy.
Future Developments:
- Global Privacy Standards: The trend towards global privacy regulations will lead to more harmonized standards for data protection.
- Increased Enforcement: Regulators will likely increase enforcement efforts to ensure compliance with privacy laws.
Challenges:
- Compliance Costs: Adapting to new regulations can be costly for businesses.
- Cross-Border Data Transfers: Navigating data privacy laws across different jurisdictions can be complex.
2. Balancing Privacy and Innovation
Description: As technology advances, there is a need to balance privacy with innovation and convenience. Emerging technologies often require access to personal data, raising concerns about privacy.
Future Developments:
- Privacy-by-Design: Integrating privacy considerations into the design and development of new technologies will become more common.
- User Consent: Ensuring that users have informed consent and control over their data will be a key focus.
Challenges:
- User Trust: Maintaining user trust while innovating can be challenging.
- Privacy Trade-Offs: Finding the right balance between privacy and functionality will require careful consideration.
Best Practices for Enhancing Financial Privacy
1. Implementing Strong Security Measures
Description: Financial institutions and individuals should adopt robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
Best Practices:
- Use Advanced Encryption: Implement encryption methods to secure data during transmission and storage.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
2. Educating Consumers
Description: Educating consumers about financial privacy and security is essential for protecting personal information.
Best Practices:
- Promote Awareness: Provide information on safe online practices and privacy protection.
- Offer Privacy Tools: Provide tools and resources for managing privacy settings and controlling data sharing.
3. Embracing Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
Description: Leverage privacy-enhancing technologies to safeguard personal information and ensure secure transactions.
Best Practices:
- Adopt PETs: Implement PETs such as zero-knowledge proofs and secure multi-party computation.
- Support Innovation: Stay informed about emerging privacy technologies and incorporate them into financial systems.